An important step after setting up your Hong Kong company is hiring employees. It is important to be aware of the legal formalities involved in the hiring process and to have a clear understanding of the employment legislation in Hong Kong.You must consider the following key issues while hiring employees in Hong Kong:Hong Kong’s employment and labor laws that have a binding effect on employers and employees;Legal restrictions and guidelines for hiring local and foreign employees in Hong Kong;Common practices and expectations in the hiring process;Hong Kong specific recruitment guidelines.Are you planning to hire employees in Hong Kong? Not sure about the employment law and employment Ordinance? This guide provides an introduction to Hong Kong’skey labor legislations, hiring guidelinesfor local and foreign employees and employee benefits, and common recruitment practicesin Hong Kong.Hong Kong Employment Ordinance
The Employment Ordinance is the key legislation that spells out the basic terms and conditions that govern employment laws in Hong Kong.
Importance of the Employment Ordinance
The Employment Ordinance is Hong Kong’s major legislation relating to labor and employment issues. It outlines the individual rights, duties and responsibilities of the employer and employee. Additionally, the Ordinance governs the details of the employment contract to ensure that the employee is adequately protected and specifies the basic terms and conditions of employment.
You must first assess if your employee is covered by the Employment Ordinance.
If the Employment Ordinance covers your employee, the employment contract terms must satisfy the minimum requirements of the Employment Ordinance.
If the Employment Ordinance does not cover your employee, the contractual terms will depend on mutual agreement between you and the employee.
 To Whom Does the Employment Ordinance Apply?The Employment Ordinance covers all employees, whether temporary or part-time, except the following:A family member who lives in the same dwelling as the employer;An employee as defined in the Contractsfor Employment Outside Hong Kong Ordinance. This Ordinance applies to employment contracts entered into in Hong Kong by employees performing primarily manual work and employees with a maximum monthly wage of HK$20,000, who are employed by foreign employers and whose employment is based outside Hong Kong.A person serving under a crew agreement under the Merchant Shipping (Seafarers) Ordinance, or on board a ship that is not registered in Hong Kong.
To Whom Does the Employment Ordinance Apply?The Employment Ordinance covers all employees, whether temporary or part-time, except the following:A family member who lives in the same dwelling as the employer;An employee as defined in the Contractsfor Employment Outside Hong Kong Ordinance. This Ordinance applies to employment contracts entered into in Hong Kong by employees performing primarily manual work and employees with a maximum monthly wage of HK$20,000, who are employed by foreign employers and whose employment is based outside Hong Kong.A person serving under a crew agreement under the Merchant Shipping (Seafarers) Ordinance, or on board a ship that is not registered in Hong Kong.An apprentice whose contract of apprenticeship has been registered under the Apprenticeship Ordinance, and who is entitled to some but not all of the protection of the Employment Ordinance.
Furthermore, the Employment Act distinguishes between employees, categorizing them as:
Employees employed under an employment contract;
Employees employed under a continuous employment contract.
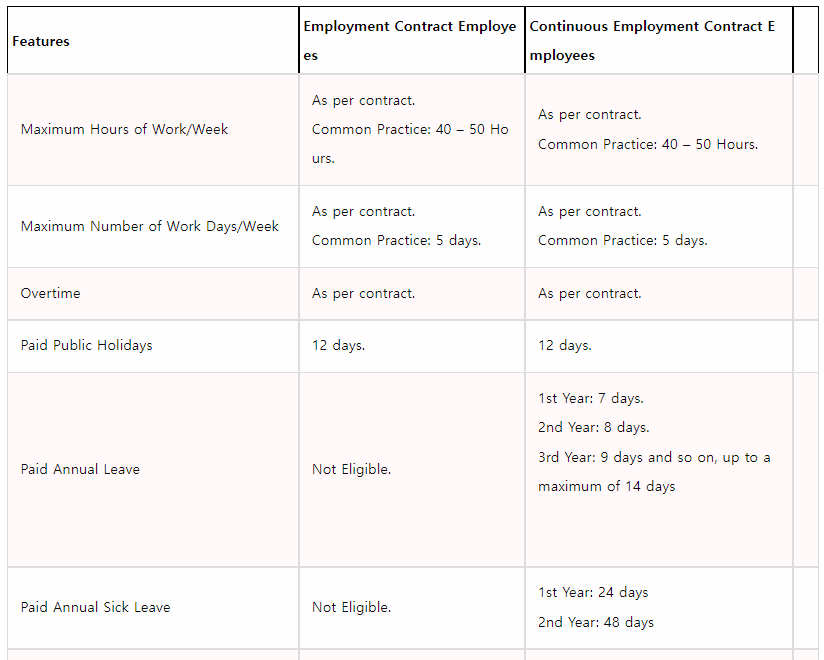
Employees employed under an employment contract are entitled to basic protection under the Ordinance including payment of wages, restrictions on wage deductions and the granting of statutory holidays, etc.



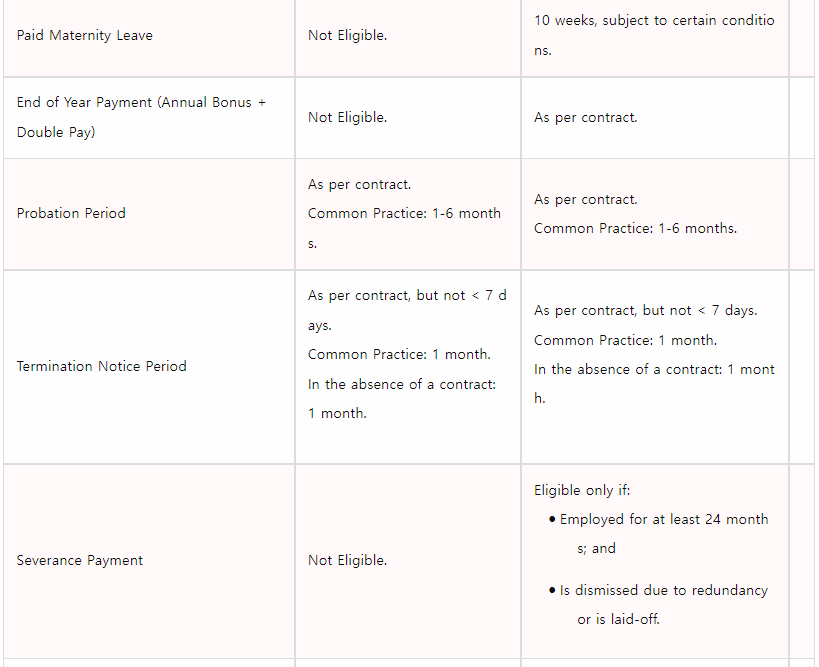
Employees employed under a continuous contract, whether temporary or part-time, are entitled to all the statutory benefits under the Employment Ordinance including rest days, paid annual leave, sickness allowance, severance payment and long service payment etc. A continuous contract of employment is an employment contract under which an employee works continuously for the same employer for 4 weeksor more, with at least 18 hoursin each week.
Key Features of the Employment Ordinance and Common Practices in Hong KongHong Kong Employers: Duties and ResponsibilitiesDrafting the Employment ContractHong Kong employment contract specifies the agreed upon terms and conditions of employment between the employer and employee. The contract includes both explicit and implied terms.Please note that if your employee is covered under the Employment Ordinance, the contract terms should abide by the minimum requirementsunder the Ordinance.Employment contracts can be oral or written. If contracts are in the written form, it is mandatory for all employers to provide employees with a copy of the written employment contract. In addition, employers must obtain their employee’s consent before making any subsequent changes to the terms of the employment contract. Some of the key pointsto be included in the contract are:Appointment position;Duration of employment contract;Obligations during employment;Date of employment commencement;
Remuneration package;
Hours of work;
Employee benefits;
Probation clause, if applicable;
Code of conduct; and
Termination
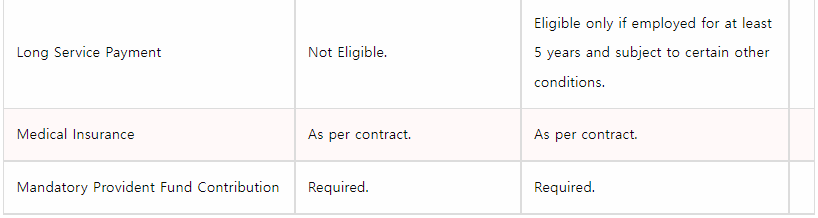
Reporting Employee Remuneration in Tax ReturnsAs an employer, you are required to prepare tax forms for all your employees to report their remuneration every year under the Income Tax Ordinance. You are also required to keep payroll records for at least seven years.
Tax Formalities for Employees Leaving Hong KongTax clearance is required for employees leaving Hong Kong for good or for a substantially long period exceeding one month. Tax clearance ensures that the departing employees have paid all taxes. Note that this does not apply to employees who travel frequently in the course of their employment. As an employer, you must notify the tax authority (Inland Revenue Department of Hong Kong) of the employee’s expected date of departure, at least one month prior to the departure date.You must also withhold all payment due to your employee from the date on which the notification was given, for a period of one month or until the IRD does an assessment and confirms that all taxes have been paid by issuing a letter of release , whichever is earlier.Contributing to the Mandatory Provident Fund (MPF) SchemeProvident fund contributions are mandatory for all employees (including full-time, part-time and casual or temporary staff) aged 18-65 years.The following employees are exempt from the MPF Scheme:Domestic employees;Self-employed hawkers;People covered by statutory pension or provident fund schemes, such as civil servants and subsidized or grant school teachers;Members of occupational retirement schemes that are granted MPF exemption certificates;
Foreigners who enter Hong Kong for employment for less than 13 months, or who are covered by overseas retirement schemes; and
Employees of the European Union Office of the European Commission in Hong Kong.
Employers and employees are each required to contribute 5% of the employee’s monthly cash income to a registered MPF Scheme.
The maximum level of monthly income for contribution purposes is HK$30,000.
Mandatory contributions are capped at HK$1,500 for employees earning more than HK$30,000 a month.
Employee contributions are not mandatory if an employee’s monthly income is below HK$7,000. However, the employer contribution is required.
A separate scale of contribution applies to casual employees who are remunerated on a daily basis.
Employers must provide monthly pay-records to each employee within seven working days after the mandatory contributions are made. Information in the pay-record should include the employee’s relevant income, the amount of contributions made and the date the contributions were paid to the scheme.

Hong Kong’s workforce is a cosmopolitan one, comprising of diverse individuals in terms of ethnicity, gender, and age. As a result, employers are encouraged to eliminate any discriminatory practices in employment. In this regard, the Labor Department has issued certain guidelines on how to prevent discrimination on the grounds of sex, disability, family status, and race in the workplace. A summary of the guidelines is as follows:Employers are advised to use consistent selection criteria for recruitment, promotion, transfer, training, dismissal and redundancy as well as terms and conditions of employment.Skills, experience and ability to perform the job should take precedence over age, race, gender, religion, family status or disability.Employees handling applications and conducting interviews should be trained to avoid acts of discrimination.Employers must review all advertising materials and accompanying literature relating to employment to ensure that such materials do not list attributes such as age, gender, marital status, race, religion and language, unless it is duly justifiable.Candidates must be short-listed based on whether their skills and capabilities match with the objective selection criteria.Application forms must avoid questions that could lead to discrimination on the grounds of age, gender, marital status, race, religion and language.
Employers must only ask questions at job interviews that relate directly to the essential requirements of the job.
Tests that are used for selection purposes must be professionally designed so that they are specifically related to the job requirements and should measure an applicant’s actual or potential ability to do the job.
The legal age to work in Hong Kong is 18 years and above. However, you are permitted to employ children and young persons aged 13 years – 17 years. Please note that there are restrictions on the type of work that children and young persons can perform. There is currently no mandatory retirement age in Hong Kong. However, in practice the retirement age is usually 60-65 years.For students who are Hong Kong citizens or Hong Kong Permanent Residents: Students who are citizens or PRs of Hong Kong can be hired on a full time or part time basis, without any restrictions. Students, including interns, are entitled to MPF contributions. The common practice is to pay interns only a monthly allowance.For students who are foreigners: Foreign students of full-time, locally accredited programs at degree level or above and whose study period is not less than one academic year can be hired as interns subject to the following conditions:The internships must be study or curriculum-related and be arranged or endorsed by the institutions where the student is studying; andThe duration of the internship is up to one academic year, or one-third of the normal duration of the relevant full-time academic program, whichever is shorter.There is no restriction on the nature of work, level of salary, location, number of working hours and employers.Moreover, these students (excluding exchange students) may take up:Part-time on-campus employment for not more than 20 hours per week throughout the year;
Employment during the summer months without any limit in relation to work hours and location.

Hiring Part-time Employees and Contractual StaffThe Hong Kong Employment Ordinance does not formally define part-time or contractual employees. However, in common practice part-time staff work for lesser number of hours than full-time employees. Contract workers generally refer to employees on a fixed-term employment contract. Under Hong Kong’s Employment Ordinance, part-timers and contract workers enjoy the same protection as permanent full-time employees.The legal age to work in Hong Kong is 18 years and above. However, you are permitted to employ children and young persons aged 13 years – 17 years. Please note that there are restrictions on the type of work that children and young persons can perform. There is currently no mandatory retirement age in Hong Kong. However, in practice the retirement age is usually 60-65 years.